Drivers are reminded to slow down use caution and check DriveBCca to plan ahead when setting out during the winter months. Summer tires are not recommended for driving between October 1 and March 31 and chains on summer tires are not an acceptable substitute for legal winter tires on signed BC.
 Commercial Vehicle Tire And Chain Requirements Province Of British Columbia
Commercial Vehicle Tire And Chain Requirements Province Of British Columbia
Aside from being winter ready drivers should ensure that they have a properly stocked emergency kit.
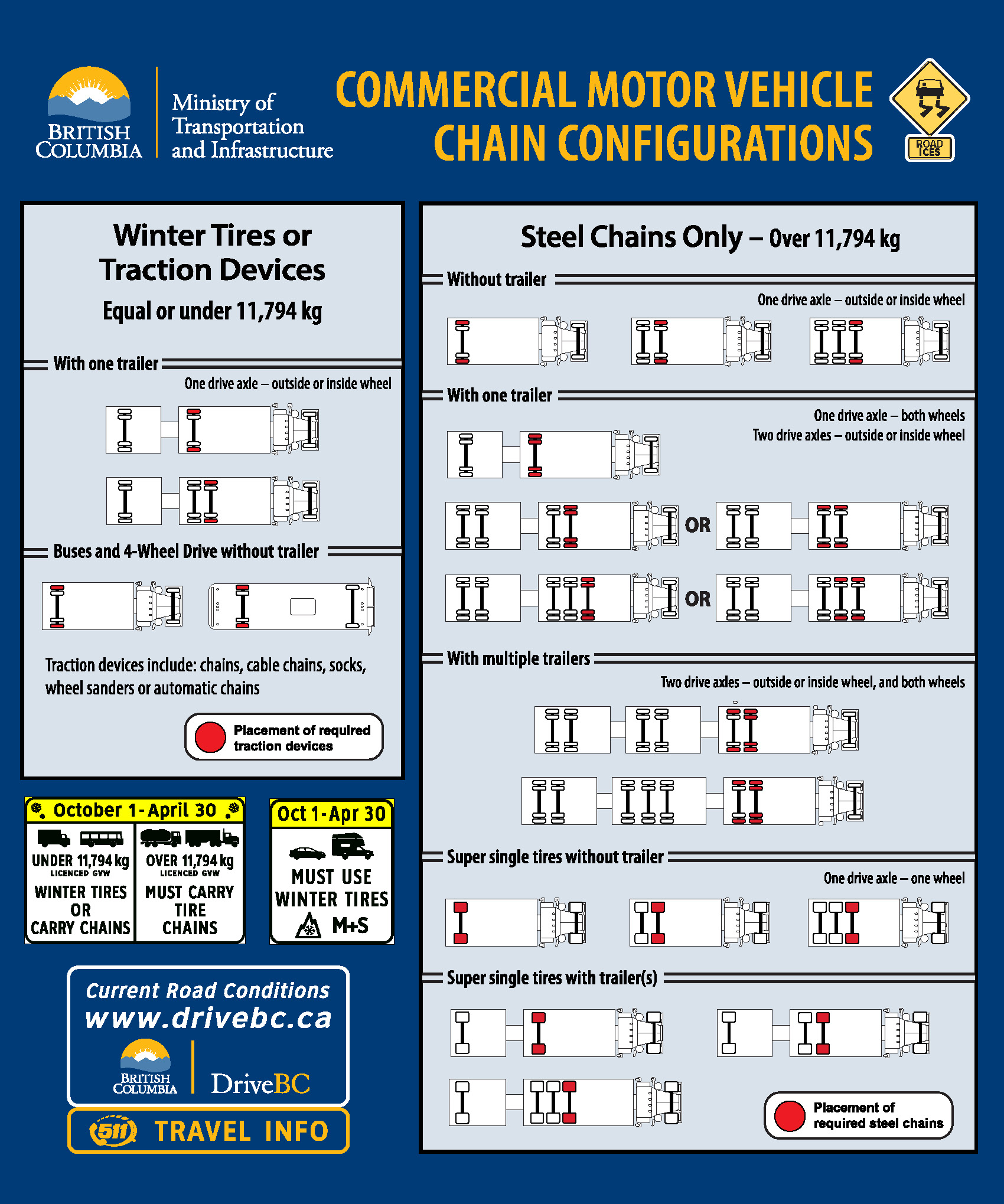
Drive bc winter tire laws. The law stipulating winter tires or to carry chains is in effect from October 1 to April 30 on all numbered highways in BC. If you pass a sign requiring the use of winter tires currently both all season marked MS on the sidewall or true winter tires marked with the mountain and snowflake symbol on the sidewall. Winter tires arent mandatory across the entire province but on most BC.
Further drivers and passengers should have extra. Drivers travelling on those highways without proper winter tires can receive a fine of 109. Winter tires or chains are required on most routes in British Columbia from October 1 to April 30.
However you must have at least two matching winter tires on the primary drive axle even when. 1 and requires drivers to equip their vehicles with winter tires if they plan to travel on certain BC. For select highways not located through mountain passes andor high snowfall areas tire and chain requirements end March 31.
For select highways not located through mountain passes andor high snowfall areas tire and chain requirements end March 31. Winter tires must be. Winter tire regulations end on March 31 on many highways however the.
Require cars and light trucks to use winter tires from October 1 to March 31. Winter tires mandatory on most BC. While the best way to stay safe in extreme weather conditions is to avoid driving the Ministry notes that there are a number of things drivers can do.
Certain highways in BC. Drive BC DriveBC September 28 2019. The province of British Columbia has not yet mandated that only true winter tread tires be used during the winter months on our highways.
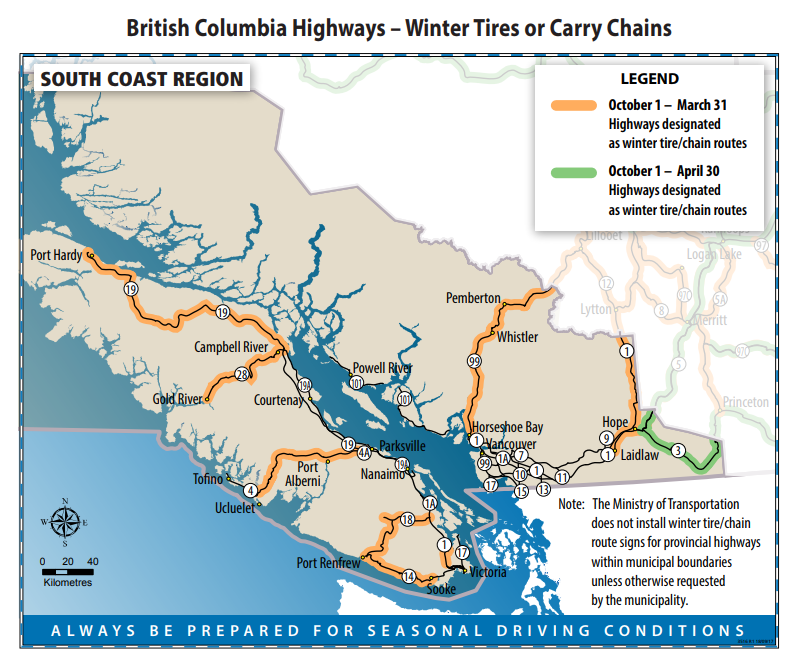
In British Columbia winter tires are defined as those labelled with either the Mountain Snowflake symbol or the Mud and Snow MS symbol the ministry said. Signs are posted on these designated highways to advise drivers where and when winter tires are required. Extending winter tire and chain regulations to end of April CTV Vancouver Published Wednesday April 4 2018 231PM PDT A snowy section of the Coquihalla is seen in this file photo.
Drivers can check out the designated winter tire and chain routes online with Drive BC. Winter tire rules in effect on BC. A legal winter tire on a standard passenger vehicle or a four-wheelall-wheel vehicle must have at least 35 mm of tread depth.
Highways starting Tuesday Globalnewsca Drivers caught without the correct tires could face a 109 fine and be. New Winter Tire Rules for BC. On October 1 2014 the Ministry of Transportation and Infrastructure announced new winter tire rules for British Columbia.
Learn more about winter tire and chain requirements in BC. 1 through March 31 drivers are required to use snow tires on most BC. Drivers must obey winter tire and chain signs throughout the province from October 1 to April 30.
Use four matched winter tires. Roadside signs state passenger vehicles are required to have winter tires and commercial trucks must carry chains on most BC highways between October 1 How to Measure Tire Tread Depth in 15 Seconds October 16 2015 11 Comments We want to show you how to measure your tires tread. Vehicles not equipped with winter tires are prohibited from travelling past the signs.
Highways in the north interior south coast and on Vancouver Island. Winter Tire and Chain-up Routes and Dates. Starting tomorrow winter tires will be mandatory on most highways in British Columbia.
Make sure that all four winter tires are evenly matched in size tread type and depth. The provincial law takes effect on Oct. Outside of the Lower Mainland.
The changes are part of the Rural Highway Safety and Speed Review conducted by the Ministry about one year ago when BC residents were asked to express their opinion. These routes are marked with regulatory signs posted on highways throughout the province.
If an employer has just cause to terminate an employee this can be done without notice or severance. Employees can take up to three days of unpaid job-protected personal illness or injury leave.
/hours-teens-are-legally-allowed-to-work-2063912_Final-f834f3e53b7c42f2b665a35092888421.png) Hours Minors Are Legally Allowed To Work
Hours Minors Are Legally Allowed To Work
Employees may be terminated from their employment in a variety of ways.
/hours-teens-are-legally-allowed-to-work-2063912_Final-f834f3e53b7c42f2b665a35092888421.png)
Labor laws bc. A week is from Sunday to Saturday. Labour Employment Law in British Columbia. Have worked or earned wages like paid vacation days or another statutory holiday on 15 of the 30 days before a statutory holiday Some people think employees only need to work the day before and the day after to qualify for statutory holiday pay.
An employee must also have at least eight hours off between shifts. If an employee works during this period eg. Labour Relations Code LRC governs the relationship between employers and their employees who are represented by a union.
Employees can quit their job at any time. If an employee quits their job theyre not paid compensation for length of employment. Employment Standards Act and Regulation to help provide a clear understanding of the law.
Labour and employment counsel provide assistance with the negotiation drafting interpretation and application of collective agreements and the development of collective bargaining strategies and labour dispute contingency plans. Sets standards for payment compensation and working conditions in most workplaces. The law in BC.
Labour and Employment law is a multi-faceted practice that pertains to all aspects of labour relations human resources and the employment relationship. An employer may lockout after serving 72-hours lockout notice on the union. Employers can end an employees job by giving written working notice or pay called compensation for length of service.
Only the first eight hours worked in a day count towards weekly overtime. This isnt the case in BC. It is not a legal document and should not be used as a substitute for legal counsel.
An employee must have at least 32 hours in a row free from work each week. Employees are paid time-and-a-half for any time worked over 40 hours worked in a week even if an employee doesnt work more than eight hours in a day. Not every work issue or type of work is related to BC.
Because of an emergency they must be paid extra pay. Such terminations are rare. The standards promote open communication fair treatment and work-life balance for employees.
To qualify an employee must have been employed for 90 calendar days. 21 1 Except as permitted or required by this Act or any other enactment of British Columbia or Canada an employer must not directly or indirectly withhold deduct or require payment of all or part of an employees wages for any purpose. In British Columbia there are numerous labour laws that apply to the workplace.
Employees must give notice to their employer if they are unable to work because of illness. Read how the rules apply to most employers on the BC. See if the standards apply to you.
Additionally disputes between employers and unions are heard before the. According to one CBC columnist if provincial governments change their labour laws in line with Ubers proposal they will cement the notion that gig workers are not employees and that they can be denied a minimum wage sick days access to employment insurance and the same rights and protections as most other workers httpsbitly3udpgVX. The Employment Standards Act sets out rules on hours of work time off notice severance pay and other topics.
Has minimum standards for wages and working conditions for most workplaces in the province. British Columbia Law Institute 1822 East Mall University of British Columbia Vancouver BC Canada V6T 1Z1 Voice. Canadian labour law is that body of law which regulates the rights restrictions and obligations of trade unions workers and employers in Canada.
Guide to the Employment Standards Act and Regulation This guide is an interpretation of the BC. Everyone who has been dismissed should seek out professional legal advice prior to signing an offer. Its strategic mission is to be a leader in law reform by carrying out.
They can also choose to give a. A Practical Guide 37. Employment Standards Act ESA regulates employees who do not belong to a union.
In order to strike a union must take a secret ballot strike vote and serve 72-hours strike notice on the employer.
One break during every period of 5 consecutive hours of work. The temporary rules continue to be in effect until July 3 2021.
 Employment And Labour Law Seminar May 6 2015
Employment And Labour Law Seminar May 6 2015
In Ontario the Employment Standards Act ESA provides most employees with one 30 minute meal break for every 5 hours of work.
Ontario labor laws breaks. 3 Most Important Employment Law Decisions of 2020 - Legally Speaking on Arbitration Clause in Employment Contract puts the Breaks on the Uber Class Action in Ontario 5 Steps to Follow After Being Fired - Legally Speaking on Ive been fired. Employment Standards Act breaks are known officially as eating periods. In Ontario most workplaces are regulated by the Ontario Employment Standards Act 2000 which sets break times in the workplace among many other things.
Under the Employment Standards Act employers must provide one thirty-minute break from work after every five hours of work. Ontarios Employment Standards Act ESA has minimum standards that employers must follow. The ESA does not require an employer to provide any breaks in addition to eating periods.
An employee who was on declared emergency leave may be eligible to take infectious disease emergency leave or another leave of absence under the Employment Standards Act 2000. The ESA requires that employers provide employees with an uninterrupted 30-minute eating period after no more than five consecutive hours of work. Employers do not have to give employees coffee breaks or any other kind of break.
This meal period must be uninterrupted. Employees may also request to split this 30 minute period into two 15-minute breaks. Work Breaks and Eating Periods in Ontario Employers in Ontario are required to provide rest periods from work.
Therefore 9 hours of work and 2 X 30-minute breaks. In most cases employees who work more than the standard hours they must be paid at the overtime wage rate. Break Times in Ontario Workplaces.
This rule however is designed to specifically address meals rather than bathroom breaks. Newfoundland and Labrador requires a one-hour break following five consecutive hours of work. This meal break must be uninterrupted and does not have to be paid.
In Ontario employees rights to time off from work such as breaks for lunch are set out in the Employment Standards Act ESA. As of February 10 2021 employees are no longer entitled to take declared emergency leave under the Employment Standards Act 2000 ESA. The only break guaranteed to employees under the Employment Standards Act is an unpaid 30-minute meal period within the first 5 hours of work.
However if the employer does provide another type of a break such as a coffee break and the employee must remain at his or her workplace during the break this time is considered to be working time under the ESA. Meal Breaks in Canada According to the ESA all employees with some exceptions are entitled to one 30-minute break within the first five hours of work. Work Break Law Ontario The law for breaks at work is governed by Section 20 of Ontarios Employment Standards Act.
Hours of Work and Breaks Standard hours of work are 40 hours per week and 8 hours per day. An employee must not work for more than five hours in a row without getting a 30-minute eating period meal break free from work. An employee who works from 8 am to 6 pm is entitled to two 30-minute breaks.
The ESA builds some flexibility into this as the employer and the employee can agree to split the 30 minutes into two eating periods provided they total 30 minutes in each consecutive five hour period. The Ontario Employment Standards Act ESA requires that employees be given a meal break of at least 30 minutes within each five consecutive work hours. In most jobs you get at least 30 minutes off after every 5 hours of work.
In this post we will focus on the law in Ontario which is set out by the Ontario Employment Standards Act 2000 ESA. An employer must provide an employee with an uninterrupted 30-minute eating period lunch break at intervals to ensure that the employee goes no more than five. An employer reserves the right to cancel breaks but only if the employee is paid to work during that 30-minute block of time.
This includes rules about hours of work and breaks. The 30-minute break is. Under the Canada Labour Code all workers have the right to take an unpaid 30-minute break after five continuous hours of work.
Employees cannot work for more than five hours in a row without being given a 30-minute eating period free from work. Your employer does not have to pay you for this time. Employees are also entitled to an unpaid 30 minute break after 5 hours of consecutive work.
Temporary ESA rules continue In response to the COVID-19 pandemic the Ontario government made a regulation that changed certain Employment Standards Act 2000 ESA rules during the COVID-19 period. If an employee is free to leave the workplace the employer does not have to pay for the time. Employment Standards Act 2000.
Legislation doesnt require additional breaks during the workday. Employees who are required to remain at the workplace during a coffee break or breaks other than eating periods must be paid at least the minimum wage for that time.
B335-04 Safety Standard for Lift Trucks. A raised truck van or car may look cool but there is no real purpose or need for it.
 Ontario S Most Recent Changes To Vehicle Safety Laws Toronto Com
Ontario S Most Recent Changes To Vehicle Safety Laws Toronto Com
This regulation will remain in place the MTO said late Monday in.
Ontario lifted truck laws 2016. The PassengerLight Duty Vehicle Inspection Standard otherwise known as Regulation 611 under the Ontario Highway Traffic Act HTA sets out which of a vehicles components and systems must be checked and what condition they must be in for a vehicle to be declared. Similarly HTA Regulation 41305 - Vehicle Weights and Dimensions. Ontario vehicle weight and dimension limits are prescribed in the Highway Traffic Act HTA and its various regulations which are administered by the Ministry of Transportation Ontario MTO.
Youll be able to haul more weight and bring you in line with the guys who have already done this Moore says. Z150 Safety Code on Mobile Cranes. Trailers are 16 years from date of manufacture.
They still dont have a clue. Landlords will be permitted to increase rent across Ontario by a maximum of 20 per cent. What the law says.
Employers have a duty under Section 252h of the Occupational Health and Safety Act to take every precaution reasonable in the circumstances for the protection of the worker but there are specific regulations governing the safe use of lifting equipment depending on your industry. And allow for an emergency lift axle override making it possible to lift a self-steering axle in emergency situations. Z248 Code for Tower Cranes.
The modifications came into force on February 5 2016. The new requirements which affect every aspect of the vehicle inspection process go into effect on July 1 2016. The word accident is used when there is a car crash.
Im not worried about it because I usually have to tell the MTO inspectors how the law works on them anyway. All non-SPIF lift axle will get allowable gross weight reductions starting 2020. ODTA SPIF vehicles are allowed higher weights while non-SPIF vehicles will be restricted to operating at lower weights.
Trucks configured to meet the SPIF requirements are allowed a gross vehicle weight rating GVWR of 36 metric tonnes while the trucks that dont comply with the rules have seen GVWRs limited to 27 tonnes. Parts VII and VIII of the Act are included as Chapters 6 of this guide book. Some have argued that it is needed for off road purposes such as agricultural uses.
View CSA Standards Cited in OHSA Regulations on the Ministrys website. So it sounds like limits will be put in place but they wont be banned entirely. Laws were brought in through a grandfathered approach.
SPIF axles have to be recalibrated every 4 years I think. 31 2020 and with a permit can extend this out further until the vehicle reaches 15 years of age. For example in the fourth and final phase any truck manufactured prior to July 1 2011 can operate under the pre-SPIF rules until Dec.
No way to find out for sure until the full legislation. Powered lift trucks are widely used in Ontario industry and as a result all three Ministry sector regulations Mining and Mining Plants Construction Projects and Industrial Establishments have provisions that deal with them. It doesnt look trucks with lift kits will straight up get prevented from passing the new inspection but it does state that new Ride Height and Air Suspension requirements.
Ontarios Ministry of Transportation MTO is showing no signs of wavering in the face of renewed pressure from dump truck operators over a decade-old weights and dimensions regulation. The recent changes extend the same tire weight allowances to wide-based single tires and dual tires when mounted on single axles. Allow boats to be hauled by stinger-steer auto carriers under the same weight and dimensional limits.
Fine but then the vehicle needs to stay off the roads. Less infrastructure damage. The rate increase is applicable to lease agreements signed between Jan.
Eliminating the use of standard lift-axles on SPIF vehicles in Ontario avoids the severe overloading of remaining axles and associated risk. The first two items were supported by National Task Force Task Force on Vehicle Weights and Dimensions VWD Policy under the Council of Ministers of Transportation and Road Safety. However they are employed in by far the greatest numbers by companies that are covered by the Regulation for.
Scores of protesters defied the lockdown to protest outside the Ontario Legislature on Thursday. Contact vwdmonitoringontarioca or 1-800-387-7736 within Ontario or 1-416-246-7166. Certain heavy truck configurations especially those equipped with rigid lift-axles cause hundreds of millions of dollars of avoidable damage to Ontario roads and bridges each.
The Ontario Dump Truck Association ODTA the organizer of the protest argues that the regulation has unfairly placed the. Since lifted trucks arent really in abundance in New York the state police informed us that they mostly look for drivers that are in violation of traffic laws rather than height of the vehicle.